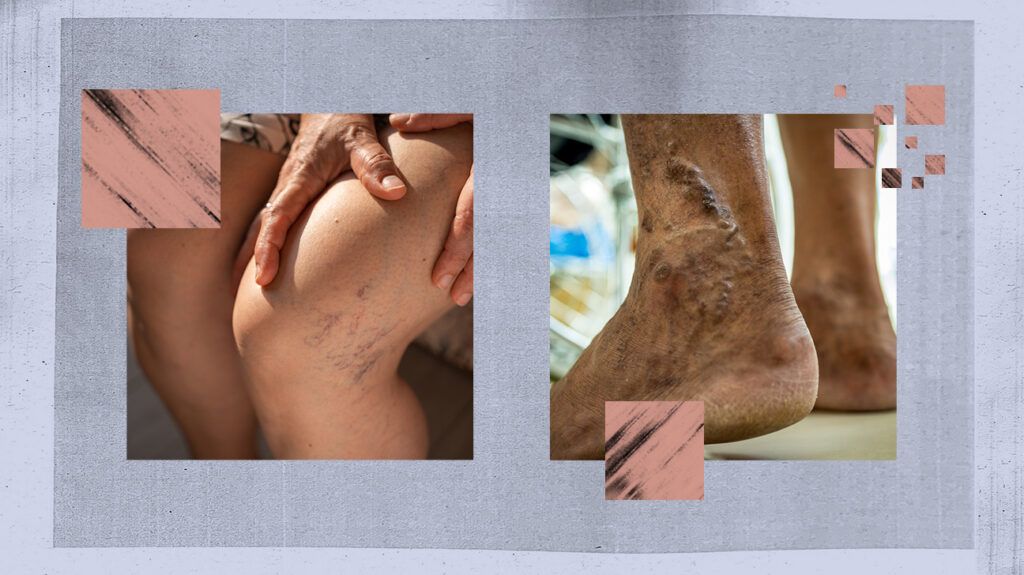
Varicose veins are twisted, swollen veins that occur due to blood buildup. They may be blue or dark purple. Treatment is not always necessary but may involve remedies such as exercise and compression stockings.
Varicose veins are a common health issue that develops when atypical or damaged valves in the veins allow blood to flow in the wrong direction or to pool. They usually develop on the legs, either on the inside of the leg or behind the knee.
The varicose veins rarely need treatment for health reasons, but if they cause swelling, aching, pain, or considerable discomfort, medical treatment and home remedies are available.
In severe cases, varicose veins may rupture or develop into varicose ulcers on the skin, requiring treatment.
Veins have
A weak valve can allow blood to leak backward and eventually flow in the opposite direction. When this occurs, blood can accumulate in a vein or veins, which then become enlarged and swollen. This
Certain lifestyle factors or health conditions may increase the risk of varicose veins.
According to a 2019 article, the following factors may increase the risk of varicose veins:
- a family history of varicose veins
- being female
- older age
- pressure on the abdomen, which may be due to:
- prolonged sitting or standing
Pregnancy and varicose veins
Pregnant people have much
A 2015 article also highlights that changes in hormone levels can lead to blood vessel wall relaxation. Both these factors may raise the risk of having varicose veins.
As the uterus, or womb, grows, there is more pressure on the veins in the person’s pelvic area. In some cases, the varicose veins may resolve after the pregnancy. However, they may sometimes remain visible.
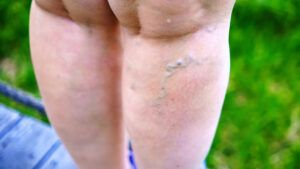

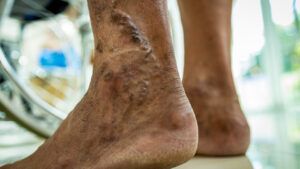
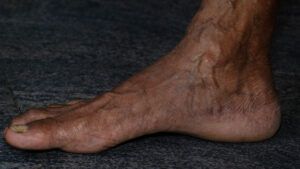
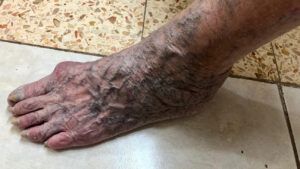
Varicose veins are twisted and enlarged veins that are
- swollen veins
- skin discoloration
- skin ulcerations
- heavy or aching legs
- itching
- tenderness
- cramps
- an intolerance to exercise
- tired legs
In
Complications of varicose veins
- pain
- venous ulcers
- superficial vein thrombosis
- deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- pulmonary embolism
- varicose eczema
- lipodermatosclerosis, a skin condition that may cause inflammation and other symptoms in the legs
People
Some complications of varicose veins, including DVT and pulmonary embolisms, are medical emergencies that require immediate treatment.
If someone has no symptoms or discomfort and does not mind the sight of the varicose veins, treatment
However, if someone has symptoms that do not improve with home remedies, they may require medical treatment to reduce pain or discomfort or to address and prevent complications.
Some people may also want treatment for varicose veins due to cosmetic reasons.
Medical treatment for varicose veins may involve the following:
- Surgical removal: Doctors may only suggest this option for someone with severe varicose veins. Surgery may involve ligation and stripping, which involves a surgeon tying up and removing the vein.
- Sclerotherapy: A doctor injects a chemical into veins, which creates scars and closes them.
- Ablation: A doctor uses radiofrequency or lasers to close up veins by heating them from the inside.
- Phlebectomy: This procedure allows doctors to remove small veins near the skin. Doctors may combine it with other treatments.
People can try the following measures at home to improve pain and prevent their varicose veins from worsening:
- getting regular exercise
- maintaining a moderate body weight
- regularly raising the legs
- avoiding prolonged standing or sitting
- avoiding restrictive clothing
People
Compression stockings squeeze a person’s legs and improve circulation. Different types are available, and wearing them every day may benefit people who cannot have surgical treatment for varicose veins.
Many people experience symptom relief when using compression stockings. However, a 2021 review suggests that more research is necessary to understand whether they can be an effective stand-alone and initial treatment or are better than other interventions.
A physical examination by a doctor
A doctor may also order a Doppler test, also known as a duplex ultrasound. This test may help them grade the severity of a person’s varicose veins.
Doctors may also check for signs of DVT during their diagnosis.
To reduce the risk of developing varicose veins, people
- getting regular exercise
- reaching or maintaining a moderate body weight
- avoiding standing still or sitting for too long
- changing positions frequently when sitting or standing for a long time
- sitting or sleeping with the feet raised on a pillow
- avoiding shoes that limit ankle movement, such as high heels
- quitting or avoiding smoking
Varicose veins are veins that become too big, swell, and twist. They typically develop when blood cannot flow as effectively. They usually affect the legs and feet but may also occur in other body parts.
In many cases, varicose veins only cause mild discomfort, and people can manage them with home remedies. These approaches include exercising regularly, maintaining a moderate weight, and avoiding sitting or standing for long periods.
If someone has varicose veins, they need to contact a doctor, even if their symptoms are not severe, to avoid serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis.


