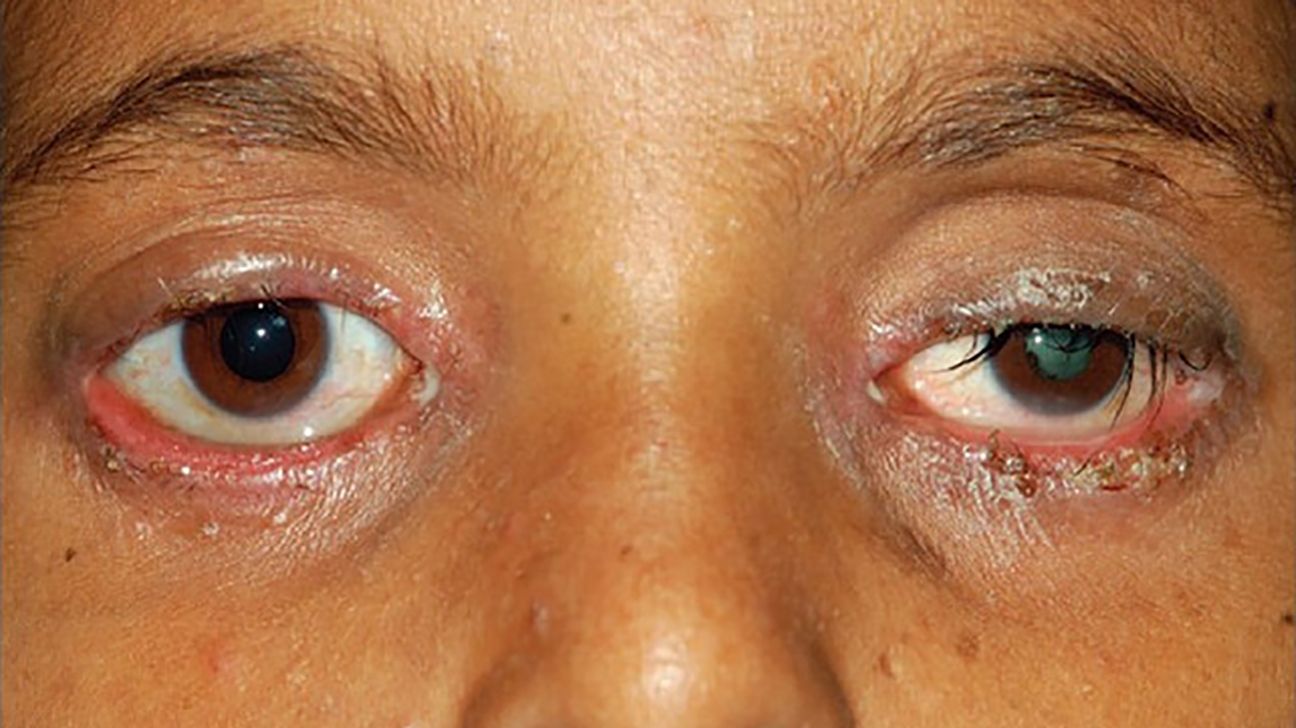
People may feel they have sticky eyes when discharge causes the eyelid to stick together. This can occur due to various conditions such as styes, conjunctivitis, and blepharitis.
The eyes can also feel sticky if a person has dry eyes, due to a lack of moisture.
Temporarily sticky eyes is usually not serious, especially when a person first wakes up after sleep. Some crustiness around the eyes in the morning is not uncommon.
But people with persistently sticky eyes, or other eye-related symptoms, should speak with a doctor.
In this article, we discuss the possible causes of sticky eyes. We also look at the treatment options and ways to prevent sticky eyes from occurring.
The eyes can feel sticky for several reasons. Sometimes, it is a result of discharge from the eyes that makes them look or feel gooey, crusty, or as though the eyelids are sticking together.
According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO), waking up with some sticky or crustiness around the eyes is normal. This discharge is the result of not blinking during the night and various debris and mucus depositing at the corners of the eyes.
Another potential cause is dry eyes, which may cause stickiness due to not having enough moisture to lubricate them.
Below are some medical conditions that may cause persistent sticky eyes.
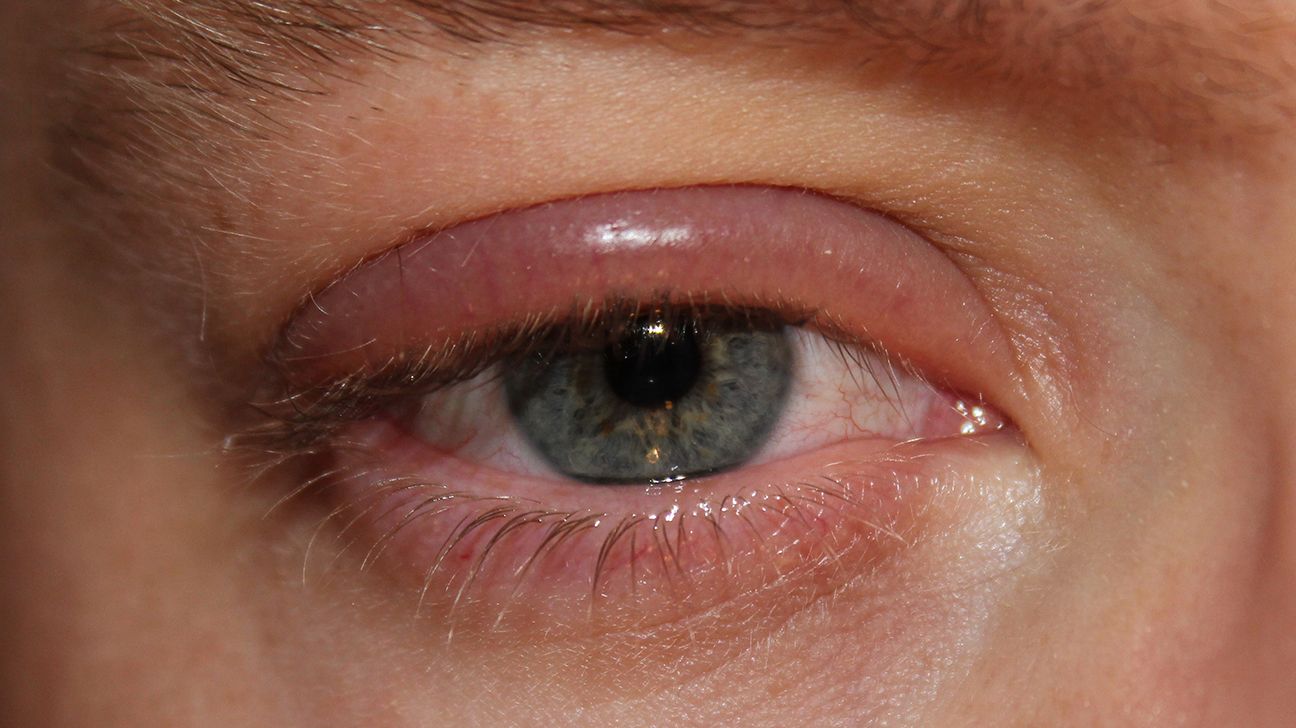
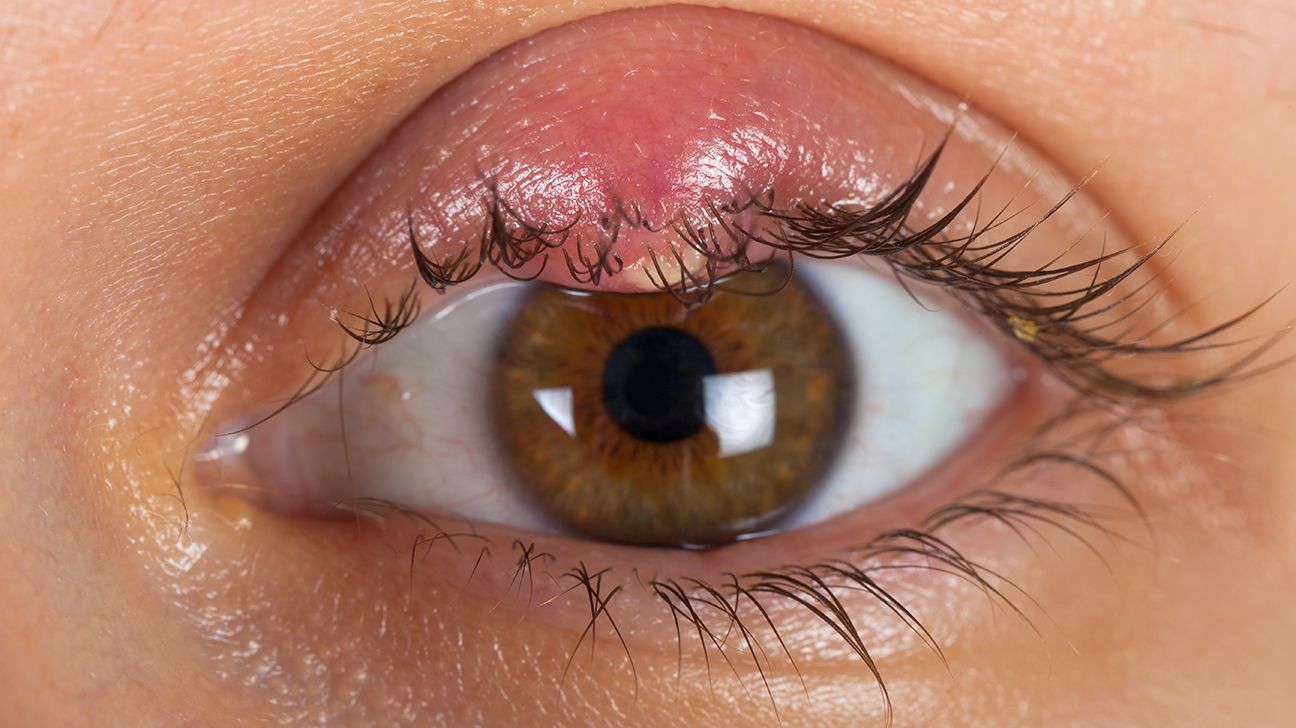
Blepharitis is a
- inflamed
- itchy
- puffy or swollen
- irritated or burning
- dry
- watery
- sensitive to light
- as though a foreign object is stuck in them
It can also cause crusty flakes to appear on the eyelashes.
There are two types of blepharitis: anterior and posterior. Anterior blepharitis develops due to bacteria on the skin or dandruff. It affects the outside of the eye, where a person’s eyelashes attach to the eyelid.
Posterior blepharitis occurs when the oil glands become clogged. It affects the inner edge of a person’s eyelid.
According to the American Optometric Association (AOA), without treatment blepharitis can lead to other issues, such as blurry vision, missing eyelashes, or secondary infections.
Treatment
Treatment can vary depending on the type of blepharitis, but it typically involves:
- warm compresses
- keeping the eyelids clean
- antibiotics for bacterial infections
- eye drops
- dandruff shampoo
- keeping the glands clean and clear
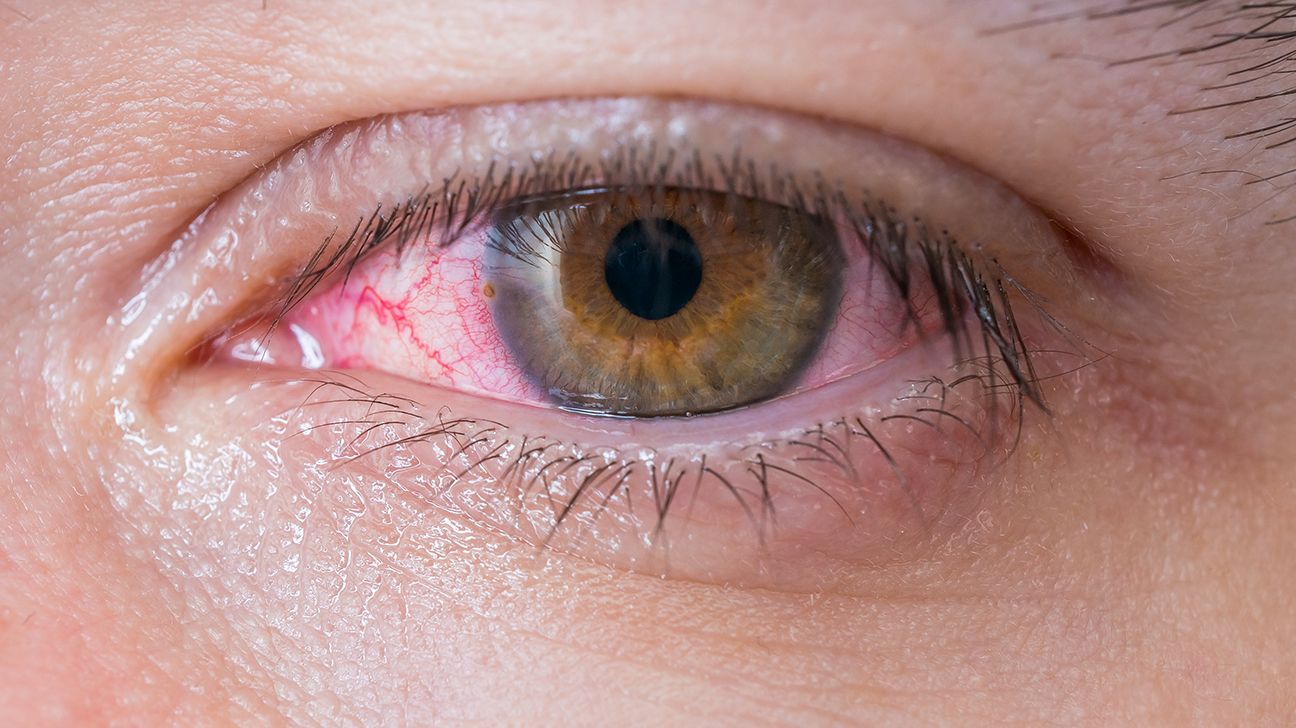
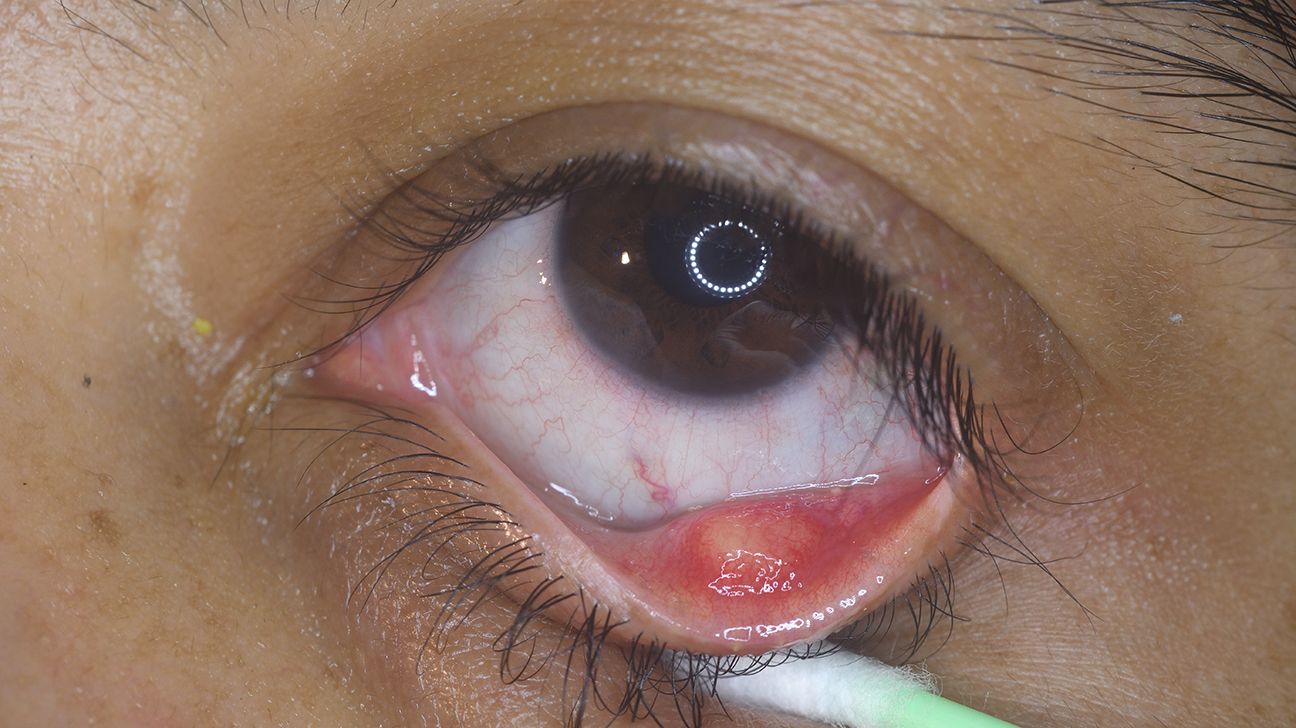
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is an infection that causes symptoms such as:
- swelling of the conjunctiva or eyelids
- pink or red color in the white of the eye
- the feeling of an object in the eye or the urge to rub the eye
- increased tear production
- difficulty wearing contacts
- crusting of the eyelids and lashes
- irritation, itching, or burning in the eye
- pus or mucus discharge
The
Treatment
Treatment for the conjunctivitis can vary depending on the cause.
For bacterial causes, a doctor may prescribe antibacterial ointment or eye drops. It is also important to take steps to prevent the spread of the infection to the other eye or to others.
Avoid wearing contact lenses and eye makeup, and do not share towels or other personal items.
Viral conjunctivitis will typically resolve without treatment, but artificial tears or cold compresses may be soothing. A person can treat allergic conjunctivitis using antihistamines and eye drops.
Parents or caregivers of children with conjunctivitis should always take them to see a doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
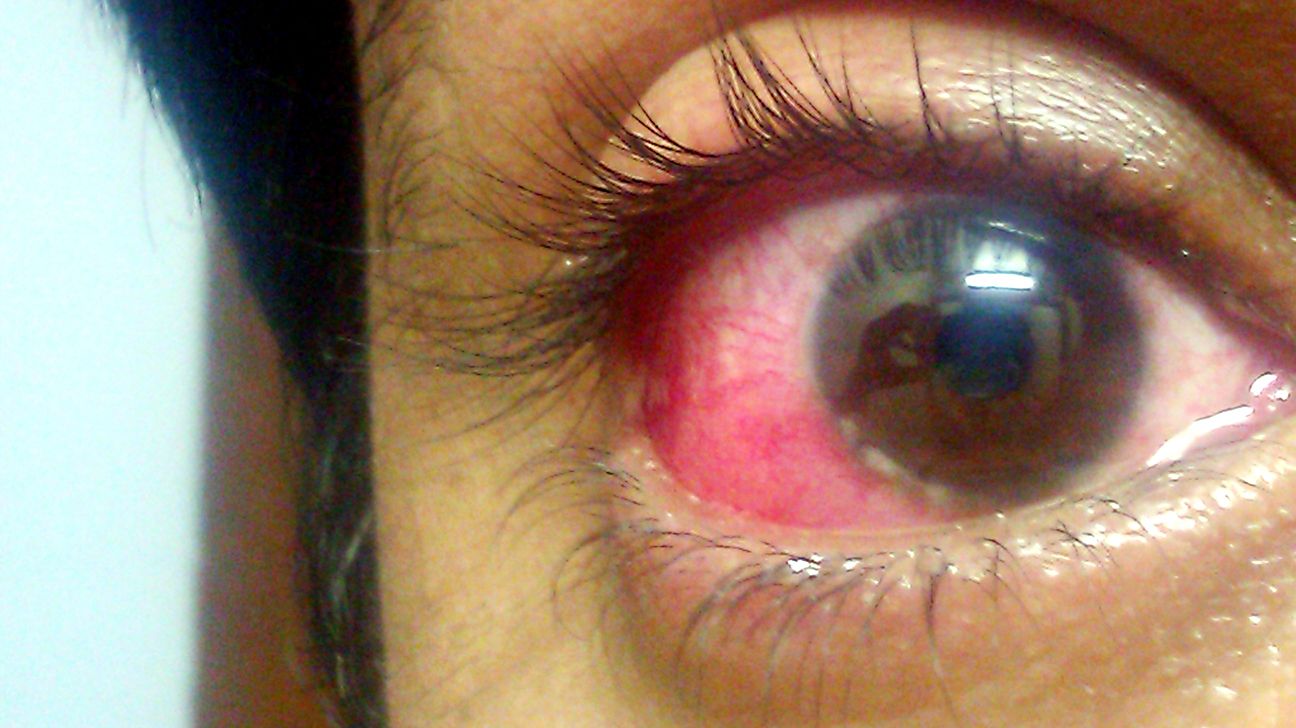
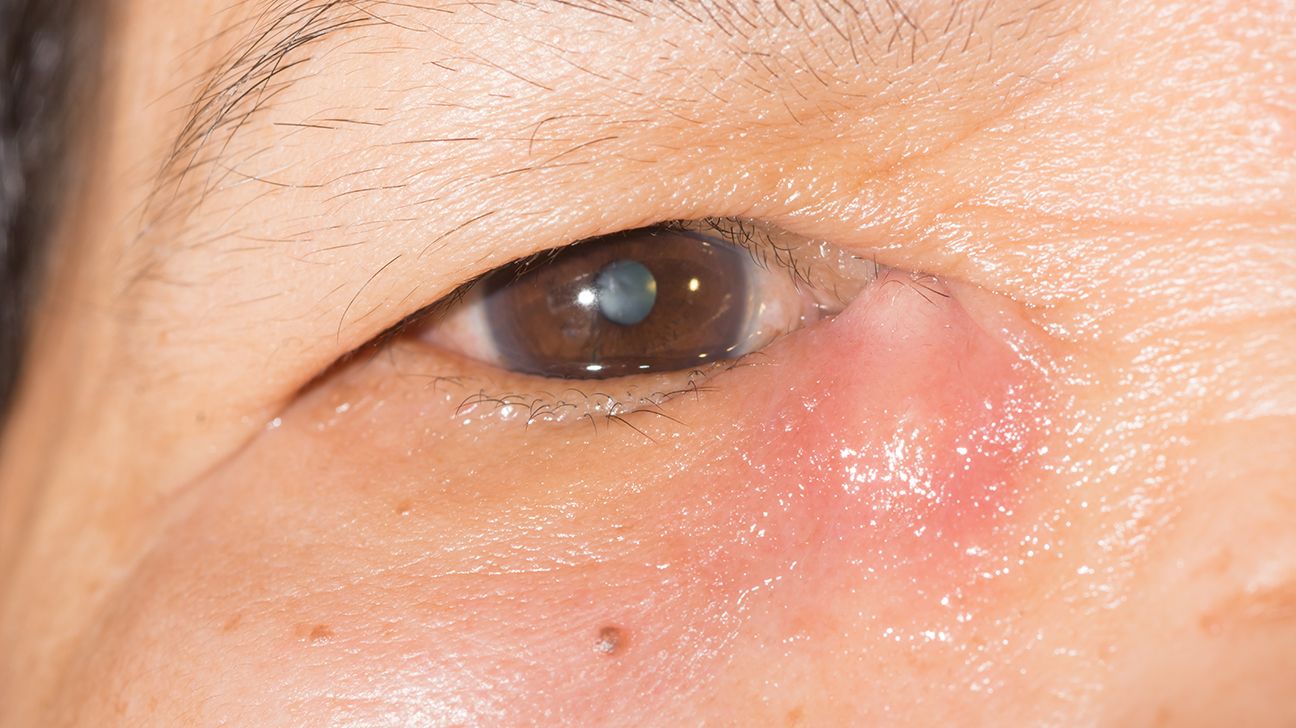
A stye is a painful bump that appears on the eyelid due to a blocked oil gland or bacterial infection. The symptoms of a stye include:
- a painful bump along the edge of the eyelid
- a small spot of pus at the center of the bump
- a scratchy sensation in the eye
- light sensitivity
- excess tearing
- crustiness along the margin of the eyelid
Treatment
Styes usually resolve on their own, but warm compresses can ease symptoms. People can also gently massage the eyelid to help express what is inside sooner.
But if there are signs of infection, it is important to see a doctor to get antibiotics.
Dacryocystitis is the infection of the lacrimal sacs, or tear sacs. It typically occurs just after birth or in adults who are
In infants, it occurs due to problems in the tear ducts, such as a blockage. In adults, it can occur due to infection, trauma, nasal abscesses, and bacteria, such as Streptococcus.
The symptoms can include:
- tenderness and swelling
- excess tears
- fever
- thick discharge from the eye
- swelling near the inner corner of the eye
Treatment
Treatment includes warm compresses and antibiotics.
A person can also perform a Crigler massage on themselves or the affected infant. They can do this by placing the index finger in the corner of the eye and rolling the finger downward. It is important to wash the hands thoroughly before and after doing this.
Chronic dry eye occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears. According to the AOA, causes can include either poor quality tears or not enough tears. Common symptoms include:
- blurry vision
- watery eyes
- burning or stinging sensation
- sensitivity to light
- redness on the whites of the eye
Treatment
Common treatments include:
- artificial tears
- warm compresses
- eyelid massage
- increasing tear production
- treating other conditions causing the issue
- conserving tears via surgery to block or close the tear ducts
Several other conditions may cause sticky eyes to form. These can include:
- unclean contact lenses
- foreign objects in the eye
- damage or injury to the eyes
A person should speak with a doctor if they experience sticky or crusty eyelids or lashes. A person’s doctor can diagnose and recommend treatment for the underlying condition, which will help the crusty eye clear.
Sticky eyes are common in newborns and young children. They can occur due to a blocked tear duct.
A parent or caregiver may notice sticky substances in the corner of the eyes or see that the eyelashes have clumped together. It can affect one or both eyes.
Although the blocked tear duct will usually clear up without any intervention, a parent or caregiver may need to clean the baby’s eyes using a clean piece of cotton wool.
According to the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS), symptoms resolve by the age of 1 in 90% of children.
However, in some cases, people may confuse a blocked tear duct with conjunctivitis. Anyone who notices discharge alongside red or pink whites of the eyes in a child in their care should take them to see a doctor.
If the whites of the eyes do not turn red or pink, the cause is likely to be a blocked tear duct.
Another cause of sticky eyes in babies is dacryocystitis. A parent or caregiver should contact a healthcare professional if they suspect this condition, as antibiotics may be necessary.
People should speak with a doctor to determine the cause of persistent sticky eyes before trying home treatments, especially if the person with symptoms is a child.
If a person has an infection, home treatment may unintentionally spread the infection to the other eye or to other people. It may also allow the problem to progress.
Depending on the cause, the following may help:
- gently cleaning the eye regularly with a soft, damp cloth
- applying hot or cold compresses
- avoiding wearing contact lenses until it gets better
- avoiding applying cosmetic products near the eyes, such as makeup or moisturizers that may be irritating
- using artificial tears, if the cause is dryness
Always wash the hands before and after touching the affected eye. If only one eye is sticky, it is important to avoid using the same washcloths or cotton pads to wipe the other eye.
The prevention of sticky eyes is not always possible, but following good eye health practices may help to reduce the risk. People can:
- keep the eye area clean
- avoid touching the eyes with unwashed hands
- regularly wash pillow cases, face cloths, and towels
- protect the eyes from harsh winds or chemicals using eye protection
- drink enough water each day
- avoid using irritating products near the eyes
People who wear contacts should follow safety routines when handling their eyes and contacts. The
- rubbing and rinsing contacts in a clean solution after each use
- using only contact solution to clean the case or contacts
- disposing of excess solution and drying the case with a clean paper towel
- washing the hands thoroughly every time before handling the contacts or eyes
A person should contact a doctor if they have persistently sticky eyes or other signs of eye or eyelid irritation, such as itchiness or swelling. Always speak with a doctor if any of these symptoms affect a baby or child.
People should also let a doctor know if their treatment for the eye condition is not working. A doctor will likely want to examine the eye and determine the cause of the continued irritation.
Sticky eyes occur when too much mucus or discharge from the eyes builds up on the eyelid and lashes, causing a crusty or sticky feeling. It can also occur due to dryness.
Numerous conditions can cause this symptom, including blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and styes. Sometimes, the cause may be an infection that requires antibiotics.
When in doubt, a person should speak with a doctor about their symptoms to determine whether further treatment is necessary.


