Scalp eczema and psoriasis may both cause a dry, itchy rash on the scalp. However, several factors differentiate the two, including the rash appearance, level of itchiness, and causes.
A clinical dermatologist will be able to tell the difference between scalp eczema and psoriasis. Receiving an accurate diagnosis is important, as treatments can differ.
Read on to learn more about the key differences and symptoms of scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis. This article also discusses possible causes, how doctors diagnose the conditions, and treatment options.
View the slideshow below for scalp eczema and psoriasis.

Warning
Contains Sensitive Content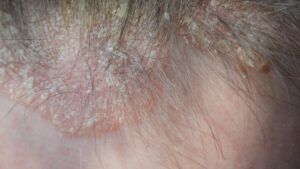
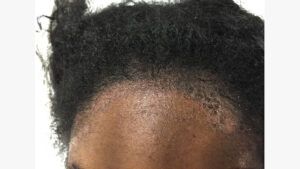
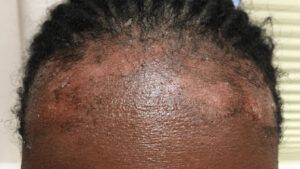
There are several ways to differentiate between scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis, including:
- Prevalence: Scalp eczema is approximately four times more common than psoriasis.
- Age of onset: Scalp eczema typically first occurs in infants and children, whereas psoriasis typically first occurs in people between the ages of 15 and 35 years.
- Appearance: Scalp eczema typically presents as dry, scaly skin with red patches on lighter skin or gray patches on darker skin. Psoriasis typically presents as thick layers with much clearer edges than scalp eczema. A person with psoriasis may experience scaly plaques that can be silvery, white, or red. A person may experience more inflammation with psoriasis than with scalp eczema.
- Itching sensation: Scalp eczema typically presents with an intense itch, whereas psoriasis typically involves a milder itch alongside a stinging or burning sensation.
Scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis are very different conditions. However, they share several similarities, including the following:
- Both conditions typically cause a dry, itchy skin rash.
- Both conditions involve the immune system but are not strictly autoimmune diseases.
- Possible triggers for both include stress, weather, certain medical conditions, some medications, and skin irritants.
- There is no cure for either scalp eczema or scalp psoriasis, but treatments can help manage symptoms.
There are some key symptoms that distinguish scalp eczema from psoriasis.
Scalp eczema symptoms
Symptoms of scalp eczema can include a dry, flaky, itchy scalp. A person may also experience inflammation, pain, and weeping of the scalp.
Several forms of eczema can affect the scalp, each with different symptoms. These include:
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Seborrheic dermatitis causes a scaly, red, or gray scalp with possible dandruff.
- Atopic dermatitis: Atopic dermatitis causes a dry, itchy scalp with inflammation.
- Allergic contact dermatitis: Allergic contact dermatitis causes an itchy, crusting, or scaly scalp with possible blisters.
- Irritant contact dermatitis: Irritant contact dermatitis causes a dry, itchy scalp with inflammation and stinging.
Scalp psoriasis symptoms
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis may include fine scaling that resembles dandruff or thick, crust-like plaques that affect the entire scalp.
Psoriasis typically has a powder-like texture and appears to have a silvery sheen.
Experts believe that scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis both result from issues with a person’s immune system.
Scalp eczema causes
Scalp eczema usually occurs when a person has an overactive immune system that responds to certain external or internal triggers.
Research suggests that a person with scalp eczema may have a gene mutation that leaves the skin more susceptible to dryness, allergies, and irritants.
There are a variety of triggers that can lead to a scalp eczema flare, such as:
- stress
- hormonal changes
- changes in the weather
- certain medications
- medical conditions such as HIV and Parkinson’s disease
- perfumes, detergents, and skin care products
- materials such as nickel and latex
- harsh chemicals
Scalp psoriasis causes
Scalp psoriasis
Psoriasis triggers include:
- infections such as streptococcal (strep) and HIV infections
- certain medications
- stress
- smoking
- obesity
- sunburn
- excess alcohol consumption
- family history
Learn more about psoriasis triggers.
To diagnose scalp psoriasis, a healthcare professional may:
- examine the scalp
- ask a person a series of questions about the symptoms
- take a full medical history
- take a skin sample for laboratory analysis
When diagnosing scalp eczema, a healthcare professional may follow similar steps. They
There is currently no cure for either scalp eczema or psoriasis. However, several treatments can help manage symptoms.
Although some treatments may be similar, what works for scalp eczema may not work for scalp psoriasis and vice versa.
The treatments for scalp eczema can include:
- emollient cream, sunflower oil, or coconut oil
- salicylic acid and tar treatments to manage thick scales
- topical steroids
- oral or topical antibiotics if scalp eczema becomes infected
- soothing or medicated shampoos
The treatments for psoriasis
- topical steroids
- tar products
- phototherapy
- medications such as biologics and immunosuppressants
There are also lifestyle changes a person can make to help manage the symptoms of scalp eczema and psoriasis, including:
- managing stress
- maintaining a moderate weight
- keeping the scalp well-moisturized
- making dietary changes, such as following the Mediterranean diet, with a doctor’s guidance
- avoiding known triggers
While scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis can look alike and share some similarities, they are very different conditions. A healthcare professional will need to diagnose each condition accurately to recommend the correct treatments.
Key differences between scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis include the appearance, age of onset, and associated itching sensation.
Neither scalp eczema nor scalp psoriasis is curable. However, there are several treatments available that can help alleviate symptoms. Making lifestyle changes may also help a person manage the symptoms of both conditions.

